MENU

Quick Set Series: Majorsine Primary INPUT Source Programming. The Quick Set Series procedure is for inverter applications where a primary input source is changed by the user of the inverter. The programmed mode is retained by the inverter processor. A future start-up will reference the saved selection. Preparing to use this feature requires the inverter to be installed with BOTH the dc voltage and ac voltage input sources. The inverter shall be powered, initial commissioning complete and...

Quick Set Series: Applications using the BATTERY function feature set in the MTS130/20AT-1U Power rectifier system. Quick Set Series Focus: Battery Mode and Battery Parameter Settings How: From the from MTS-Com Front Panel Administrator Menu Key Steps: Select DC Limits – Screen will display the High and Low threshold limits for DC output parameters. o Press the DOWN arrow button twice to move the cursor to the Ext Equipment screen o Highlight BATT/LOAD (default is Load) and...
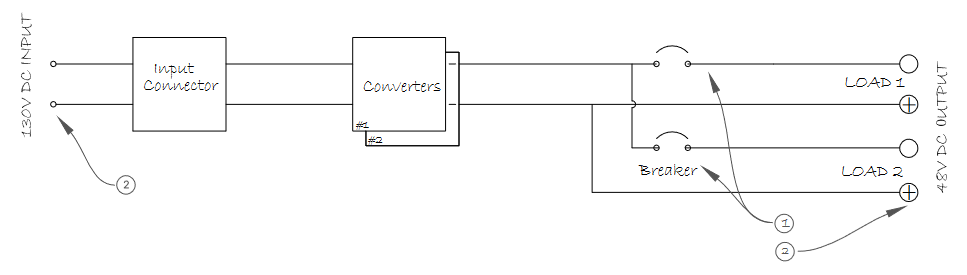
PA202.1: Single Converter System using the MTD48/50-130-1U converter power system. DC/DC Power Architecture Series Cynosure: • DC power supply to single point apparatus, possible distribution sub-panel to individual loads/over-current-protection-devices. Single steady state output voltage. • DC power supply to A/B connections utilizing the dual-output circuit breakers. This pre-configured system will operate in 100% duty cycle mode to convert 130vDC to 48vDC. The system kit includ...
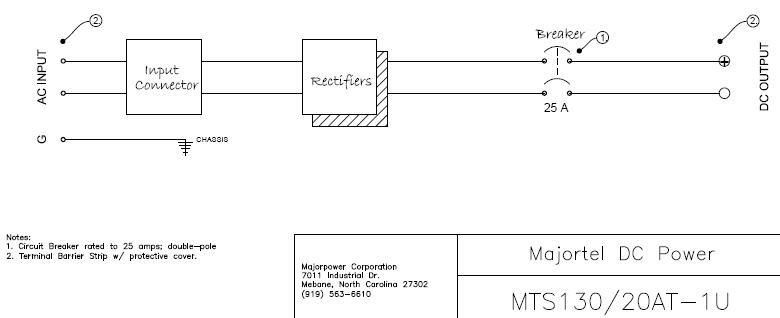
PA401.3: Load or Battery @ 125 Volt DC using the MTS130/20AT-1U rectifier power system. Power Architecture Series Cynosure: • DC power supply to single point apparatus, possible distribution sub-panel to individual loads/over-current-protection-devices. Single steady state output voltage. • DC charge supply to a specific battery connection or dc bus with temperature compensation feature active to regulate the output voltage. This pre-configured system can operate in one of two mode...